St. Pete Location
Bradenton Location
Patient Education
We're passionate about helping people achieve their healthiest, happiest skin. Whether you're struggling with acne, eczema, rosacea, or any other skin concern, we're here to offer support, information, and inspiration.
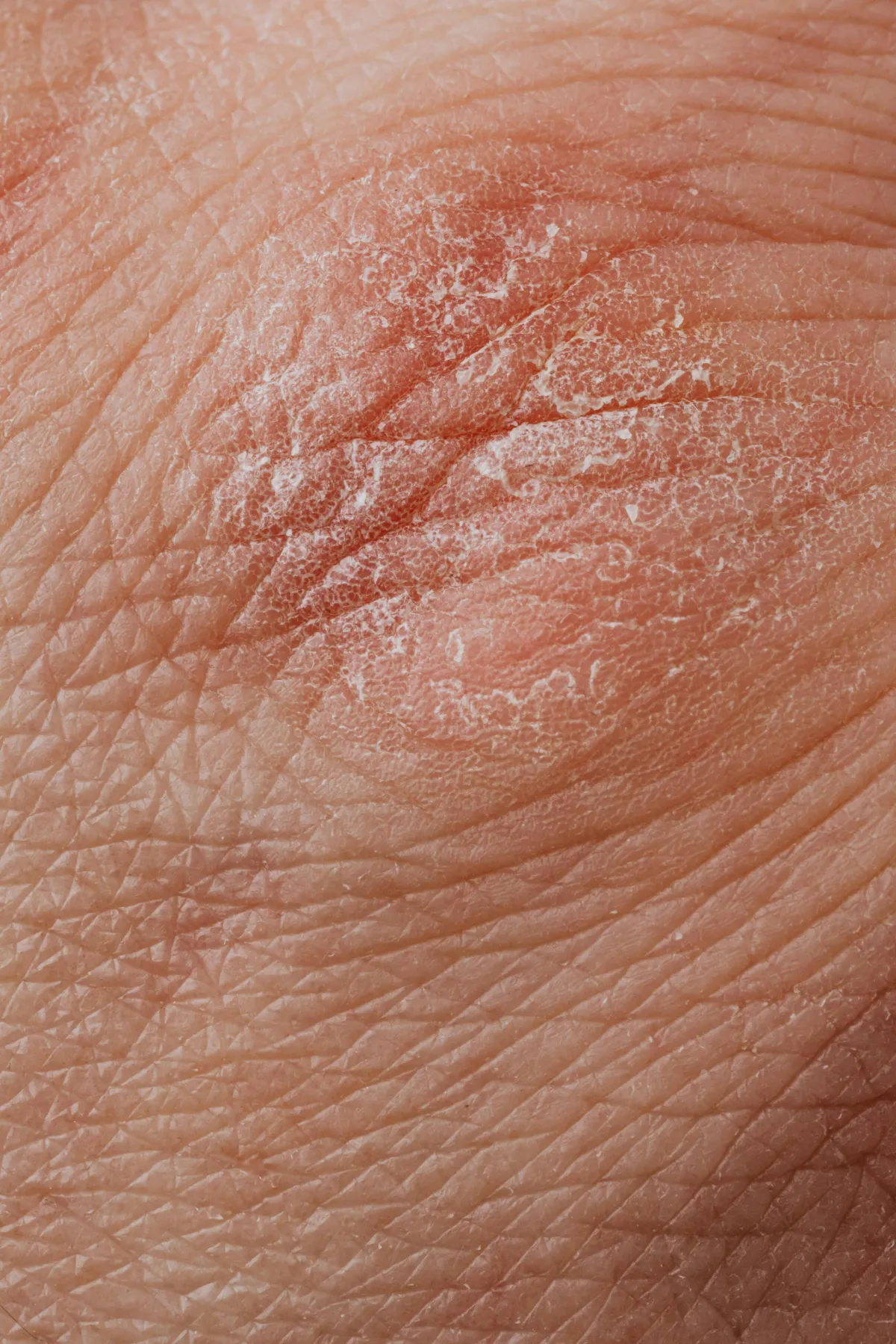
Skin Deep: Understanding Common Skin Conditions and Diseases | Leah Michel APRN, FNP-BC
Skin Deep: Understanding Common Skin Conditions and Diseases
In the realm of dermatology, a vast array of skin conditions and diseases can affect individuals of all ages. Recognizing and understanding these conditions is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of various skin ailments, offering insights into their causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
Common Skin Conditions and Diseases
Acne and Related Conditions
Acne:
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, affecting people of all ages. It occurs when hair follicles are clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads often affecting adolescents and young adults. Hormones, genes, and bacteria are key factors in acne development (Heng & Chew, 2020).
Acne Keloidalis, on the other hand, is a form of acne that primarily affects the back of the neck and is characterized by keloid-like bumps. Acne Keloidalis may be more common in individuals with a genetic predisposition (Zhang et al., 2023).

Infections and Infestations
1. Bacterial Infections
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection causing redness, warmth, and swelling. Tuiasosopo et al. (2023) found that cellulitis incidence was 1.8% among patients, with the condition predominantly affecting males and individuals over 40 years old.
Impetigo is a contagious bacterial skin infection causing red sores. he American Academy of Family Physicians (2021) notes that impetigo is a highly contagious infection characterized by red sores that can rupture and ooze, often requiring topical or systemic antibiotics for effective treatment.
Folliculitis and Boils (Furuncles):
Bacterial folliculitis and boils are common bacterial infections worldwide that cause inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding tissue. While some cases of folliculitis may heal on their own, others can develop into boils if left untreated. Boils, also referred to as furuncles, affect nearby tissue and can lead to more severe conditions such as cellulitis or lymphadenitis (Lin et al., 2021). They are painful, pus-filled bumps that form under the skin when bacteria infect and inflame one or more hair follicles. Both conditions require different treatment approaches, ranging from topical treatments to surgical drainage.
2. Fungal Infections
Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by Candida yeast, often affecting the skin, mouth, or vagina. Sharma and Chakrabarti (2023) provide a comprehensive overview of the contemporary status of invasive candidiasis, discussing its epidemiology and the challenges presented by emerging yeast infections. This infection can lead to various symptoms, including itching and discomfort, and is particularly concerning in immunocompromised individuals. Effective treatment strategies are crucial for managing candidiasis and preventing its complications.
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection causing discolored patches on the skin. Tinea versicolor typically presents as light or dark patches that may appear on the trunk, shoulders, and arms, and it is often more noticeable after sun exposure (Bhat et al., 2023).
Tinea Infections:
Tinea infections are fungal infections of the skin, hair, and nails (e.g., athlete's foot, ringworm). These infections are primarily caused by dermatophytes, which thrive in warm and moist environments, leading to a variety of clinical manifestations. The increasing incidence of dermatophyte infections, along with emerging antifungal resistance, highlights the need for effective management strategies (Sahoo et al., 2024).
3. Parasitic Infestations
Lice:
Lice is a parasitic insect that infest the hair and scalp. Meinking and Taplin (2021) explain that lice are parasitic insects that infest the hair and scalp, primarily affecting children and leading to itching and discomfort. Kress and Kress (2022) highlight that lice infestations, including head lice, body lice, and pubic lice, are common worldwide and can lead to secondary infections due to scratching.

Scabies:
Scabies are a contagious skin infestation caused by mites. The condition is characterized by intense itching and a rash, which can lead to secondary bacterial infections if left untreated (Walton & Currie, 2020).
Dermatitis (Inflammation of Skin)
Dermatitis is a broad term for skin inflammation, comprising several subtypes with distinct characteristics. Dermatitis herpetiformis, a blistering skin condition, is strongly linked to celiac disease (Antiga & Caproni, 2015). Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition causing scaly, red patches, often on the scalp, face, and chest (Borda & Wikramanayake, 2015). Perioral dermatitis is a rash around the mouth, resembling acne (Wollenberg et al., 2018). Nummular dermatitis presents as coin-shaped, itchy rashes on the skin (Wollenberg et al., 2018).

Contact Dermatitis:
Contact Dermatitis is a skin reaction to irritants or allergens, leading to inflammation, redness, and itching in affected areas. This condition can be triggered by various substances, including chemicals, metals, and plants, and can significantly impact an individual's daily life and well-being (Schnuch et al., 2022). Proper identification of the causative agent and avoidance of triggers are crucial for effective management and prevention of recurrences.
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Atopic Dermatitis is a chronic skin condition often associated with allergies, characterized by dry, itchy skin that can lead to significant discomfort and impact quality of life. This condition typically begins in childhood but can persist into adulthood, affecting millions of individuals globally (Eichenfield et al., 2022). Effective management strategies, including the use of moisturizers and topical corticosteroids, can help alleviate symptoms and reduce flare-ups.
Subtypes of Dermatitis:
Dermatitis Herpetiformis:
These are linked to celiac disease, causes blistering. Shields et al. (2020) highlight that more than 90% of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis have an associated gluten-sensitive enteropathy, although only a minority present with classic gastrointestinal symptoms at diagnosis (Shields et al., 2020).
This causes scaly patches, often on scalp and face. Blauvelt (2023) highlights that a new topical drug, roflumilast foam, demonstrated promising results in clinical trials, with a substantial percentage of patients experiencing clearing or partial clearing of their seborrheic dermatitis symptoms (Blauvelt, 2023).
Perioral dermatitis is a rash around the mouth that resembles acne and is often triggered by factors such as prolonged use of topical corticosteroids (Hägglund et al., 2023). Kumar et al. (2022) note that the condition typically presents as red, scaly patches and can also appear around the nose and eyes, leading to confusion with other skin disorders like rosacea.
Nummular Dermatitis are coin-shaped itchy rashes. Effective management typically involves the use of topical corticosteroids alongside proper skin care practices (StatPearls, 2024).
These are small, itchy blisters on the palms and sides of the fingers. Venkatesh et al. (2024) report on a case of dyshidrotic eczema successfully treated with upadacitinib, highlighting the challenges of managing this chronic condition. Calle Sarmiento and Chango Azanza (2020) describe dyshidrotic eczema as a recurrent vesicular eruption that primarily affects the palms and soles, emphasizing its intense pruritus.
Understanding Skin Conditions and Seeking Professional Help
Many of these skin conditions can be effectively managed with proper diagnosis and treatment. If you're experiencing any skin concerns, it's essential to consult with a dermatologist for accurate evaluation and personalized recommendations.
Introducing Leah Michel: Your Trusted Skin Care Specialist
At My Skin St. Pete, we are proud to have Leah Michel as our esteemed skin care specialist and aesthetic injector. With her expertise and passion for dermatology, Leah offers a wide range of cosmetic treatments to enhance your skin's health and appearance.
Leah Michel's Expertise
Skin Cancer Screening: Leah is highly skilled in identifying and diagnosing skin cancers, ensuring early detection and treatment.
Full Body Skin Exams: She conducts comprehensive skin examinations to assess your overall skin health and identify potential issues.
Cosmetic Treatments: Leah offers a variety of cosmetic treatments, including:
Botox: Reduce wrinkles and fine lines for a more youthful appearance.
Fillers: Restore volume and enhance facial features.
Other Aesthetic Procedures: Explore additional options to address specific skin concerns.
Why Choose Leah Michel?
Personalized Approach: Leah tailors her treatments to your individual needs and goals.
Cutting-Edge Techniques: She stays up-to-date with the latest advancements in dermatology.
Compassionate Care: Leah is dedicated to providing a comfortable and welcoming experience.

Schedule Your Appointment Today
To experience the expertise of Leah Michel and My Skin St. Pete, schedule your appointment today. Our friendly staff is ready to assist you in scheduling a consultation and addressing your skin care needs.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for educational and information purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a licensed medical provider and follow their recommendations regardless of what you read on this website. If you think you are having a medical emergency, dial 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Links to other third-party websites are provided for your convenience only. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms of use for those websites. Neither My Skin by Leah Michel, APRN, FNP-BC, nor any contributor to this website, makes any representation, express or implied, regarding the information provided on this website or any information you may access on a third-party website using a link. Use of this website does not establish a doctor-patient relationship. If you would like to request an appointment with a health care provider, please call our office at (727) 295-7223.
References:
Tuchayi, S. M., Makrantonaki, E., Ganceviciene, R., Dessinioti, C., Feldman, S. R., & Zouboulis, C. C. (2015). Acne vulgaris. Nature reviews Disease primers, 1(1), 1-20.
Cui, J., Zhu, Y., Du, H., Liu, Z., Shen, S., Wang, T., ... & Liang, Z. (2023). Chromosome-level reference genome of tetraploid Isoetes sinensis provides insights into evolution and adaption of lycophytes. GigaScience, 12, giad079.
Wondafrash, A. H., Lima, U. L., Abebe, D., & Negash, K. S. (2023). Incidence and Causes of Cellulitis Among Patients at Tupua Tamasese Meaole Hospital in Upolu, Samoa in 2019. Cureus, 15(11).
Espinosa, K., & Brown, S. R. (2021). Serum lactate testing to predict mortality in patients with sepsis. American Family Physician, 103(5), 309-310.
Lin, H. S., Lin, P. T., Tsai, Y. S., Wang, S. H., & Chi, C. C. (2021). Interventions for bacterial folliculitis and boils (furuncles and carbuncles). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (2).
Sharma, M., & Chakrabarti, A. (2023). Candidiasis and other emerging yeasts. Current Fungal Infection Reports, 17(1), 15-24.
Vinolo-Gil, M. J., Herrera-Sánchez, C., Martin-Vega, F. J., Martín-Valero, R., Gonzalez-Medina, G., & Pérez-Cabezas, V. (2022, August). Eficacia de la tele-rehabilitación en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica: una revisión sistemática. In Anales del Sistema Sanitario de Navarra (Vol. 45, No. 2). Gobierno de Navarra. Departamento de Salud.
Kruithoff, C., Gamal, A., McCormick, T. S., & Ghannoum, M. A. (2023). Dermatophyte infections worldwide: increase in incidence and associated antifungal resistance. Life, 14(1), 1.
Espinosa, K., & Brown, S. R. (2021). Serum lactate testing to predict mortality in patients with sepsis. American Family Physician, 103(5), 309-310.
Hebert, A. A., Bobonich, M. A., Rodriguez Capriles, C., Gallo, G., Li, L., Somani, N., ... & Becker, E. M. (2022). Higher rates of skin clearance and efficacy in challenging body areas are associated with better health‐related quality of life following ixekizumab maintenance treatment in pediatric patients with plaque psoriasis. Pediatric dermatology, 39(1), 55-60.
Mulchandani, R., Jones, H. E., Taylor-Phillips, S., Shute, J., Perry, K., Jamarani, S., ... & Wyllie, D. H. (2020). Accuracy of UK Rapid Test Consortium (UK-RTC)“AbC-19 Rapid Test” for detection of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection in key workers: test accuracy study. bmj, 371.
Antiga, E., & Caproni, M. (2015). The diagnosis and treatment of dermatitis herpetiformis. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 257-265.
Borda, L. J., & Wikramanayake, T. C. (2015). Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff: a comprehensive review. Journal of clinical and investigative dermatology, 3(2).
Wollenberg, A., Barbarot, S., Bieber, T., Christen‐Zaech, S., Deleuran, M., Fink‐Wagner, A., ... & Ring, J. (2018). Consensus‐based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) in adults and children: part I. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 32(5), 657-682.
Dickel, H. (2023). Management of contact dermatitis. Allergo Journal International, 32(3), 57-76.
Eichenfield, L. F., Stripling, S., Fung, S., Cha, A., O’Brien, A., & Schachner, L. A. (2022). Recent developments and advances in atopic dermatitis: a focus on epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatment in the pediatric setting. Pediatric Drugs, 24(4), 293-305.
Shields, B. E., Gelfand, J. M., Allen-Taylor, L., & Rosenbach, M. (2020). Prevalence of dermatitis herpetiformis within the iCureCeliac Patient-Powered Research Network—patient characteristics and dietary counseling. JAMA dermatology, 156(12), 1374-1376.
Johnson, J. L. (2023). Seborrheic Dermatitis—What the Latest Research is Saying, From How it Develops to Current Treatments and More.
Teng, Y., Ren, M., Ding, Y., Yang, X., Fan, Y., & Tao, X. (2023). A case of perioral dermatitis successfully treated with abrocitinib. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 3035-3038.
Lockhart, M. K., & Siegfried, E. C. (2022). Evolving landscape of systemic therapy for pediatric atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Clin, 40(2), 137-43.
Robinson, C. A., Love, L. W., & Farci, F. (2022). Nummular Dermatitis. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
Venkatesh, S., Fakhraie, S., & Chovatiya, R. (2023). Recalcitrant Dyshidrotic Eczema Successfully Treated With Upadacitinib. Dermatitis: contact, atopic, occupational, drug, 34(6), 569.
Sarmiento, P. M. C., & Azanza, J. J. C. (2020). Dyshidrotic eczema: a common cause of palmar dermatitis. Cureus, 12(10).
If you have any questions or concerns about your skin & would like to schedule an appointment at our St. Pete dermatology office or Brandenton dermatology office, please call us today!
St. Pete Location
111 2nd Ave NE., Suite 1406
St Petersburg, FL 33701
Plaza Tower- Downtown St Pete
Phone: (727) 295-7223
Bradenton Location
4301 32nd St. W., Suite D2
Bradenton, FL 34277
Phone: (941) 330-5805







